Most of the tropical fish in domestic aquariums up to almost 99% of them are wildly caught and transported to the retailers and wholesalers within 24-48 hours.
Removing fish suddenly from their natural habitat exposes them to stress from which some of them die. Moreover, during transportation some marine fish those that survive could have diseases and pass the same to the fish already in the aquariums.
Adaptation to the new environment could be a bit problematic and so their defense mechanism is often weakened to an extent that they are more susceptible to diseases. This is why the quarantine tank are very important.
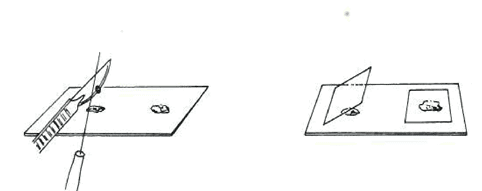
Using a microscope, the skin and gill smears or fins and gill parts are examined in seawater on slides. In seawater, the structure of cells, bacteria and parasites remain intact while they can be damaged in freshwater. However, freshwater can be used to examine internal organs.
Many large-scale symptoms of diseases are very similar and can easily lead to mistaken choice of drug treatment, with possibly harmful consequences.
Microscopic review of the diseases gives one a clear concept of the disease.
Materials:
- Two dissecting needles
- One small and one large pair of scissors
- One scapel with replaceable blades
- One sharp and one blunt pincer
- Eye-dropper containing aquarium water
How to kill fish:
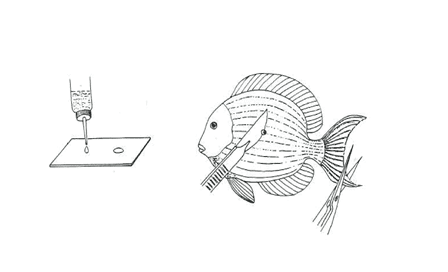
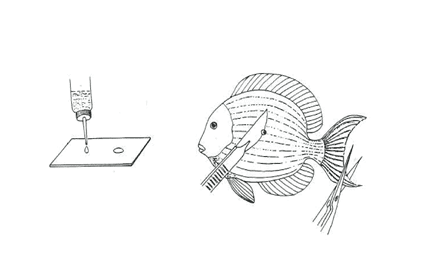
The fastest and the surest way to kill fish to cut deeply into its neck with a knife or scissors.
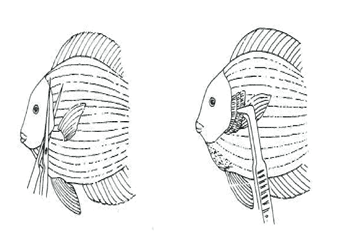
To detect pathogens on skin or skill, carefully scrap the mucus layer with a scalpel and place it into aquarium water on a slide then cover with the cover slip.
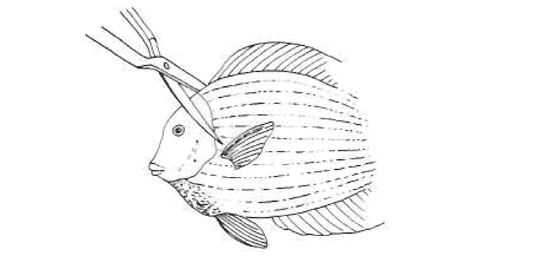
Afterwards, the gill cover can be cut away to expose the gill. Some gill tissue can be removed with the scissors or pincers, placed into a drop of seawater on a slide, and covered by a cover slip.
If necessary, the fish can be dissected:
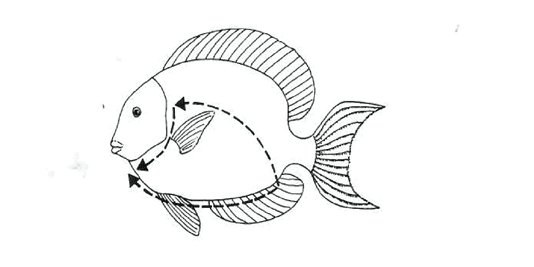
- Cut the stomach open, with scissors, from anus to gills without damaging the internal organs.
- Beginning with the anus, open up the side of the fish to the edge of the gill cover.
- After removing cut skin, the internal organs are exposed for examination.